Water Holding Capacity (WHC) and Cook Loss of Fish Muscle Application Note
This application note provides information on specific application methods and the use of Hettich products. (more…) read more...
File size: 561.2 kb
The determination of the water holding capacity (WHC) is an established method of investigating the degree of denaturation of proteins in muscle tissue. Although the emphasis to date has been on raw material, the method described here and the corresponding sample cups have been specially developed for cooked samples.
Where convenience meals are prepared from fish products, for example, the quality of the fish must be kept at a high level. Quality controls are therefore essential at various stages in the production process. Heating in particular causes changes to muscle tissue through denaturation of the proteins. The fish muscle should not disintegrate after cooking and remain tender.
A determination of the WHC and cook loss allows conclusions to be drawn about the degree of denaturation of the proteins and therefore the quality of the fish. It is, therefore, an objective and reproducible method.
Hettich products to determine the WHC and cook loss of fish muscle:

Advantages of the Method
This method enables the WHC and cook loss of heat-treated samples to be determined precisely. The methods used to date have been for investigation of raw samples and are unsuitable for a study of the kinetics of cook loss and the WHC of cooked samples since these require rapid and uniform heating of the sample.
The special design of the newly developed sample cups ensures that heat is transferred quickly and uniformly from the heating medium to the sample. The changes in quality as a result of the heating can, therefore, be determined precisely and the manufacturing processes changed where necessary.
The new formula described by Skipnes et al. factors the cook loss into the calculation of the total WHC (WHCTOT) directly.
The Sample Cup
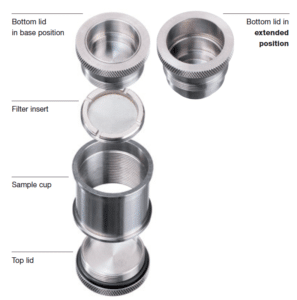
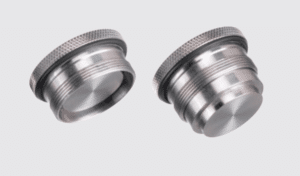
Preparation
Note: The filter and the sample should be in good contact, but the sample must not be subject to any pressure.
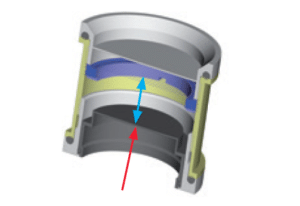
Note: Ensure that no air bubbles form on the sample cup in the water bath as they would prevent uniform heat exchange.
Steps 4 and 5 are omitted for the determination of the WHC of raw samples.
Calculations
The cook loss is the difference between the g3 value and the g4 value. The weight of the sample is given by g2 minus g1. The percentage weight loss can, therefore, be calculated from these values.
The WHC of raw samples is calculated as the ratio of the water remaining after centrifugation to the initial water content of the sample, using the following formula2):
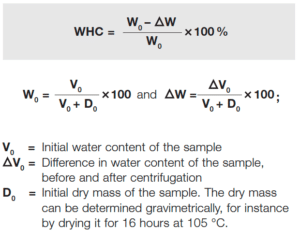
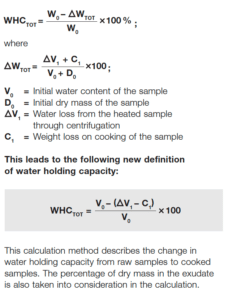
The fish sample loses liquid when it is cooked. The liquid comprises water, dissolved proteins, ash, salt, and fat. The remaining dry material D1 is therefore somewhat less than the initial dry mass D0.The sample will lose not just water but also additional dry mass during the centrifugation procedure. As a result, the remaining dry mass D2 after heating and after centrifugation will be significantly lower than D0.This method calculates the water holding capacity on the basis of the water content of the raw sample and takes into account the weight loss on cooking as the total loss WHCTOT:
Hettich products are designed to help you achieve optimal results for your application and are built to perform to the specifications outlined in the operators manual. For application-specific information and settings, please refer to your organization’s standard operating procedure. As always, our Hettich representatives are here to help determine which Hettich products and accessories best fit your laboratory requirements.

This application note provides information on specific application methods and the use of Hettich products. (more…) read more...

This product sheets provides a comprehensive overview of the unique product features specific to the model. (more…) read more...
Hettich manufactures centrifuges for any standard laboratory application.