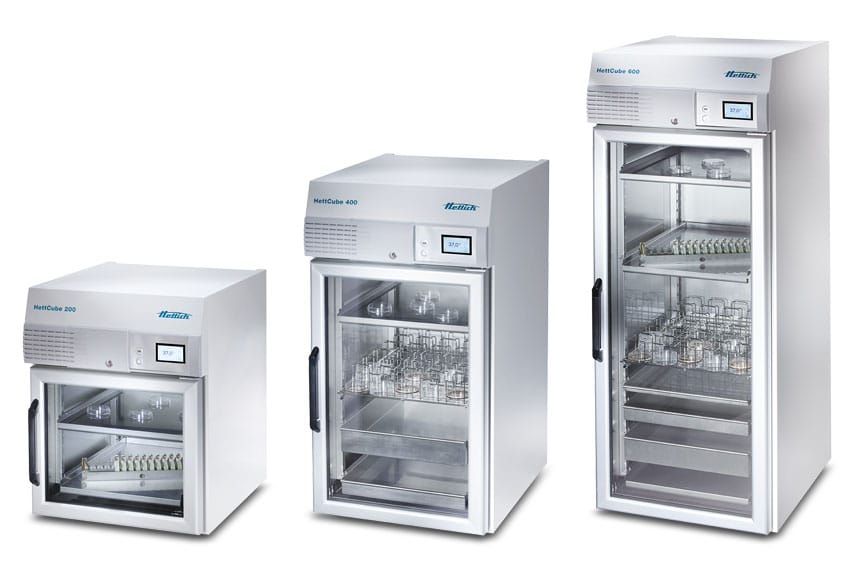
The use of HettCube incubators to detect the presence of Escherichia coli in drinking water
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a bacterium that is present in the body of both animals and humans. It is part of the normal healthy intestinal flora. However, if E. coli bacteria are ingested through food or water or come into contact with mucosa, then infections may result and can lead to sepsis. If the bacteria have undergone mutation, they can cause life-threatening diseases (e.g. EHEC) through highly toxic metabolic products.
E. coli plays an important role as an indicator organism in water analysis. If its presence is demonstrated, then it can be assumed that the water sample is contaminated with other fecal organisms. Drinking water must be absolutely free of E. coli, i.e. no organisms present in 100 ml.
METHODS OF DETECTION
The presence of E. coli is determined by the method given in EN ISO 9308-1:2000 in tryptophan broth after filtration and culture on TTC agar (Fig. 1). If E. coli is present in the broth, the addition of Kovac’s reagent will cause a color change to red (Fig. 2).
Importance of the test for the presence of E. coli in practice.
Drinking water is tested at regular intervals to protect consumers. One such test is for the presence of E. coli. The nature and frequency of the tests are laid down in national regulations such as the Trinkwasserverordnung” [Drinking Water Act] in Germany and the Safe Drinking Water Act in the USA.
Incubation conditions in accordance with EN ISO 9308-1:2000
ADVANTAGES OF HETTCUBE INCUBATORS
- Maximal validated usable space on a small footprint
- 4.3-inch touch display for intuitive operation
- Very homogeneous and stable temperature, as well as precise temperature control
- True “one-hand-operation” and flexible positioning of the shelves
- Minimal energy consumption of < 0.06 kW/h at 37 °C
- Low noise level of ≤ 44 dB(A)
- Optimized loading capacity through unique accessories and options